Securing your website on cloud hosting is crucial for protecting sensitive data, maintaining user trust, and ensuring the smooth operation of your online presence. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to secure your website, blending technical details with engaging tips to keep things interesting.
Importance of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is a modern solution for web hosting that utilizes virtual servers to host websites and applications. Unlike traditional hosting, where resources are limited to a single physical server, cloud hosting distributes data across multiple servers, ensuring flexibility, scalability, and reliability. Here’s why cloud hosting is important:
Key Benefits:
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows you to easily scale resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility ensures your website can handle traffic spikes without downtime or performance issues.
- Reliability: With data distributed across multiple servers, cloud hosting offers high uptime and redundancy. If one server fails, others take over, minimizing downtime.
- Performance: Cloud hosting typically provides faster load times and better performance due to its distributed nature and the use of advanced infrastructure.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing models enable businesses to pay only for the resources they use, making cloud hosting cost-effective, especially for startups and small businesses.
- Global Reach: Cloud hosting providers often have data centers worldwide, allowing you to serve content faster to a global audience by choosing servers closest to your users.
- Advanced Security Features: Leading cloud hosting providers invest in state-of-the-art security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and DDoS protection, offering a high level of security for hosted websites.
Step-by-Step Process of Securing Website on Cloud Hosting
1. Choose a Reputable Cloud Hosting Provider
Why It Matters: Your security starts with the foundation. A reputable provider offers robust security features, regular updates, and reliable customer support.
Steps:
- Research Providers: Look for reviews, security certifications, and customer feedback.
- Evaluate Security Features: Ensure they offer firewalls, DDoS protection, and regular security patches.
- Check Compliance: Ensure they comply with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS.
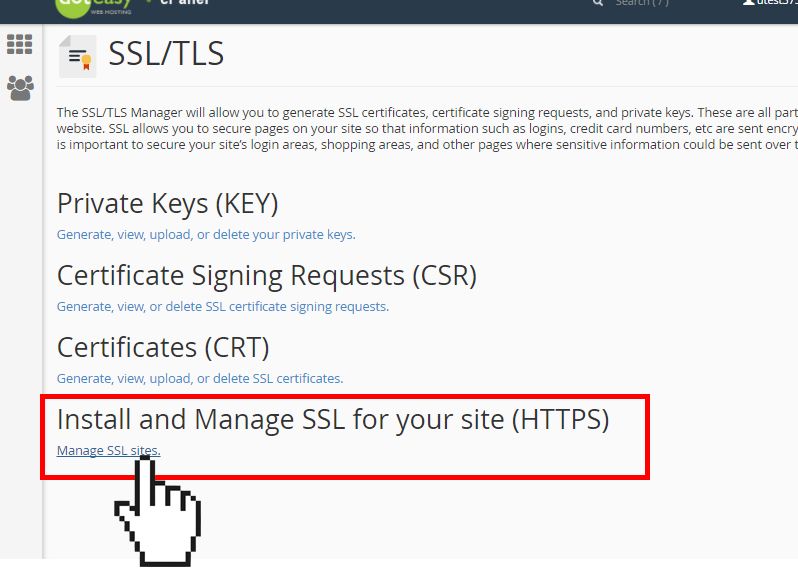
2. Enable SSL/TLS Certificates
Why It Matters: SSL/TLS encrypts data transmitted between your server and users, protecting it from interception and tampering.
Steps:
- Purchase or Obtain a Free Certificate: Providers like Let’s Encrypt offer free SSL certificates.
- Install the Certificate: Most hosting providers offer automated installation, but manual installation might be required for custom setups.
- Force HTTPS: Redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS using .htaccess or server configuration files.
3. Regular Software Updates
Why It Matters: Outdated software is a common entry point for attackers. Regular updates close security vulnerabilities.
Steps:
- Enable Automatic Updates: For your CMS, plugins, and themes.
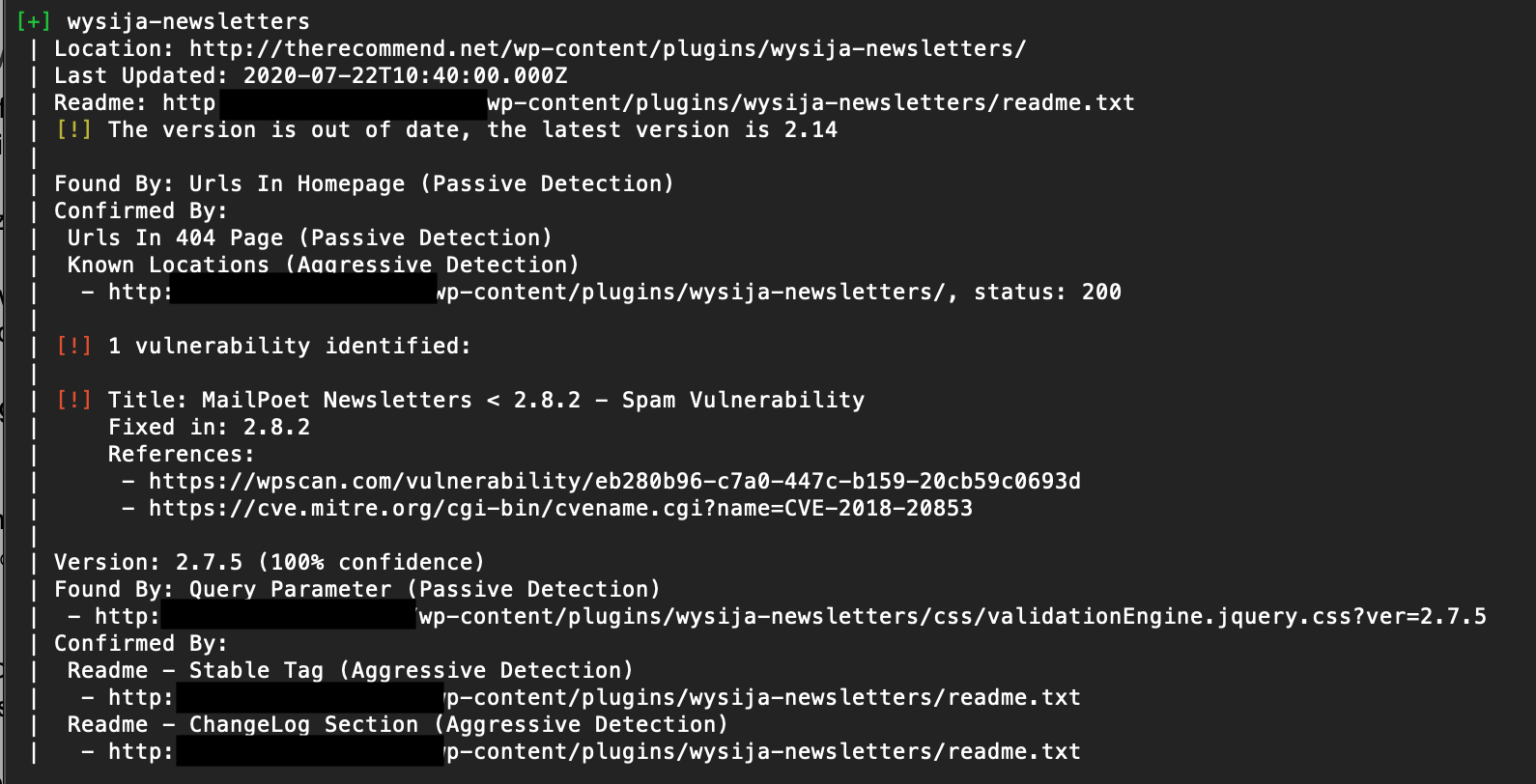
- Manually Check for Updates: Regularly verify that all software components are up to date.
- Monitor for Vulnerabilities: Use services like WPScan or Joomla Security Scanner for real-time alerts.
4. Implement Strong Authentication Measures
Why It Matters: Weak passwords and poor authentication processes can easily be exploited.
Steps:
- Use Strong Passwords: Combine letters, numbers, and symbols. Consider using a password manager.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification.
- Limit Login Attempts: Prevent brute force attacks by restricting the number of failed login attempts.
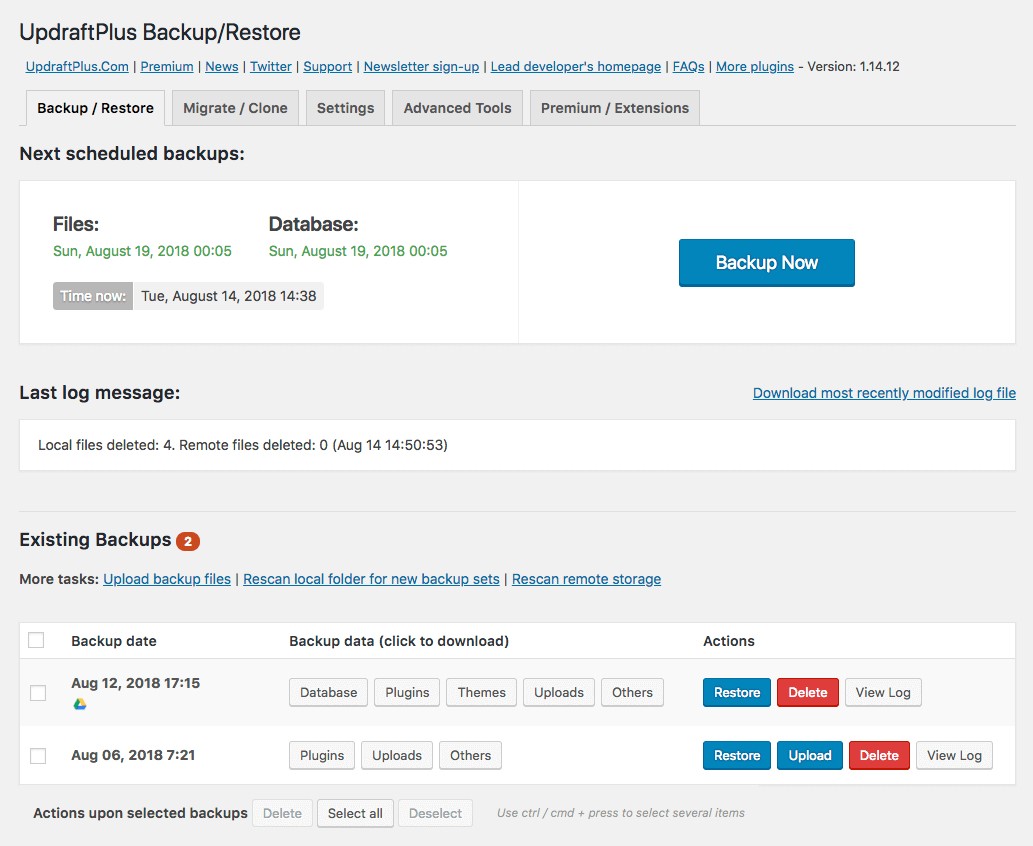
5. Regular Backups
Why It Matters: Backups are your safety net. In case of a breach or data loss, you can restore your site to its previous state.
Steps:
- Automate Backups: Use your hosting provider’s backup services or plugins like UpdraftPlus or BackupBuddy.
- Store Backups Securely: Ensure backups are stored offsite and encrypted.
- Test Your Backups: Regularly verify that backups can be successfully restored.
6. Secure Your Web Applications and Server
Why It Matters: Securing your applications and server prevents unauthorized access and mitigates vulnerabilities.
Steps:
- Harden Server Configurations: Disable unnecessary services and ports.
- Use Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Protect against common threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
- Secure Database Access: Restrict database access to necessary users and use strong passwords.
7. Monitor and Respond to Threats
Why It Matters: Continuous monitoring allows you to detect and respond to threats promptly.
Steps:
- Set Up Monitoring Tools: Use services like Sucuri or Cloudflare to monitor for suspicious activity.
- Analyze Logs: Regularly review server and application logs for unusual behavior.
- Establish an Incident Response Plan: Prepare for security breaches with a plan that includes identification, containment, eradication, and recovery steps.
8. Educate Your Team
Why It Matters: Human error is a leading cause of security breaches. Educating your team minimizes this risk.
Steps:
- Conduct Regular Training: Ensure your team is aware of the latest security practices and phishing tactics.
- Create a Security Policy: Develop and enforce a comprehensive security policy.
- Promote a Security-First Culture: Encourage team members to report suspicious activities and follow best practices.
9. Implement Content Delivery Network (CDN) Security
Why It Matters: A CDN enhances website performance and security by distributing content across various servers.
Steps:
- Choose a Secure CDN Provider: Ensure they offer security features like DDoS protection and SSL support.
- Configure CDN Settings: Optimize security settings to protect against malicious traffic.
- Monitor CDN Performance: Regularly review performance and security reports.
10. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Why It Matters: Proactive measures like audits and testing help identify and fix vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Steps:
- Schedule Regular Audits: Perform comprehensive security audits quarterly or annually.
- Hire Professional Penetration Testers: Engage experts to simulate attacks and uncover weaknesses.
- Act on Findings: Implement recommendations from audits and tests promptly.
Pros and Cons of Securing a Website on Cloud Hosting
Securing a website on cloud hosting comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Understanding these can help you make an informed decision about whether cloud hosting is the right choice for your website.
Pros:
Advanced Security Tools:
- Integrated Security Solutions: Cloud providers offer comprehensive security tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and automatic security updates.
- Encryption: Data encryption both at rest and in transit is standard practice, protecting sensitive information from interception and breaches.
Scalability of Security Measures:
- Dynamic Security Scaling: As your website grows, you can easily scale security measures to match the increased traffic and data flow.
- Adaptive Threat Management: Cloud platforms often use machine learning to detect and mitigate emerging threats in real time.
Managed Services:
- Professional Management: Many cloud hosting providers offer managed services, including regular security audits, monitoring, and maintenance.
- Expert Support: Access to expert support teams helps quickly resolve security issues and implement best practices.
Compliance and Certifications:
- Regulatory Compliance: Leading cloud providers comply with international standards and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, ensuring your website meets legal requirements.
- Regular Audits: Providers conduct regular security audits and assessments to maintain high-security standards.
Cons:
Shared Responsibility:
- Security Gaps: While cloud providers offer robust security infrastructure, the responsibility for securing applications, data, and user access lies with the website owner. Misconfigurations or user errors can lead to vulnerabilities.
- Complex Management: Managing security in the cloud requires a good understanding of both the cloud platform and security best practices, which can be challenging for less experienced users.
Potential for Misconfigurations:
- Human Error: Incorrect configurations of cloud services can expose sensitive data or create security gaps. This is a common risk that requires careful management and regular reviews.
- Overwhelming Choices: The plethora of security settings and tools can be overwhelming, making it difficult to choose the right configuration.
Dependency on Provider:
- Reliance on Provider Security: You depend on the cloud provider for the underlying infrastructure’s security. Any breach or failure on their part can impact your website’s security.
- Vendor Lock-in: Migrating to a different provider can be complex and risky, potentially leading to security vulnerabilities during the transition.
Costs:
- Security Features Costs: While basic security is often included, advanced security features and managed services can be expensive.
- Unexpected Charges: Mismanagement of resources and services can lead to unexpected costs, especially if security measures like DDoS protection are triggered frequently.
Conclusion
Securing your website on cloud hosting involves a multi-layered approach, combining technical measures, continuous monitoring, and team education. By following these steps, you can create a robust defense against cyber threats, ensuring your website remains secure and trustworthy. Remember, security is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and adaptation to new threats. Stay proactive, and keep your digital assets safe!

