Migrating your website to cloud hosting can feel like embarking on an exhilarating adventure. With promises of enhanced performance, improved scalability, and cost-efficiency, cloud hosting offers a modern solution to meet the dynamic demands of today’s digital landscape. However, just like any great expedition, this journey comes with its challenges—especially when it comes to preserving your hard-earned SEO. Ensuring a seamless transition without compromising your website’s search engine rankings requires careful planning and execution. Let’s explore the pros and cons of cloud hosting migration and understand the potential impact on SEO.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth transition:
1. Plan Your Migration
a. Conduct an Audit:
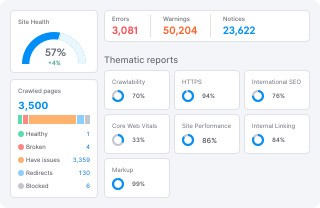
- Perform a comprehensive SEO audit of your existing site. Use tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and SEO auditing tools (e.g., Ahrefs, SEMrush).
- Document your current rankings, organic traffic, and backlinks.
b. Choose the Right Cloud Hosting Provider:
- Evaluate providers (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure) based on reliability, speed, and scalability.
- Consider the location of data centers to minimize latency.
c. Backup Your Website:
- Create a full backup of your website, databases and backup of files and configurations.
2. Set Up the Cloud Environment
a. Configure the Server:
- Set up your cloud server with the necessary resources (CPU, RAM, storage).
- Install and configure the required software (e.g., web server, database server).
b. Optimize for Performance:
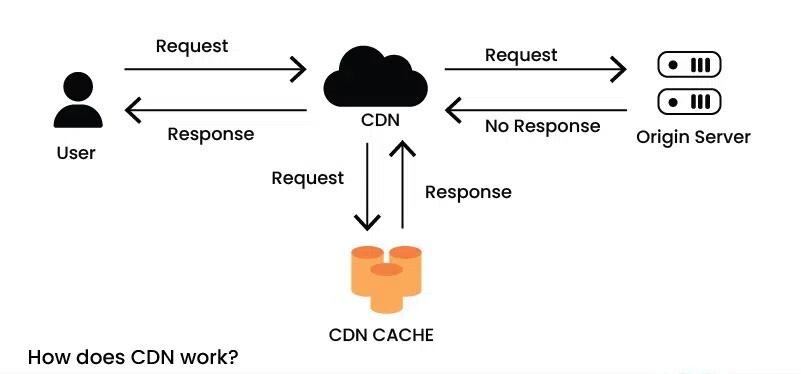
- Use content delivery networks (CDNs) to serve content faster.
- Implement caching mechanisms (e.g., server-side caching, database caching).
3. Transfer Your Website
a. Migrate Data:
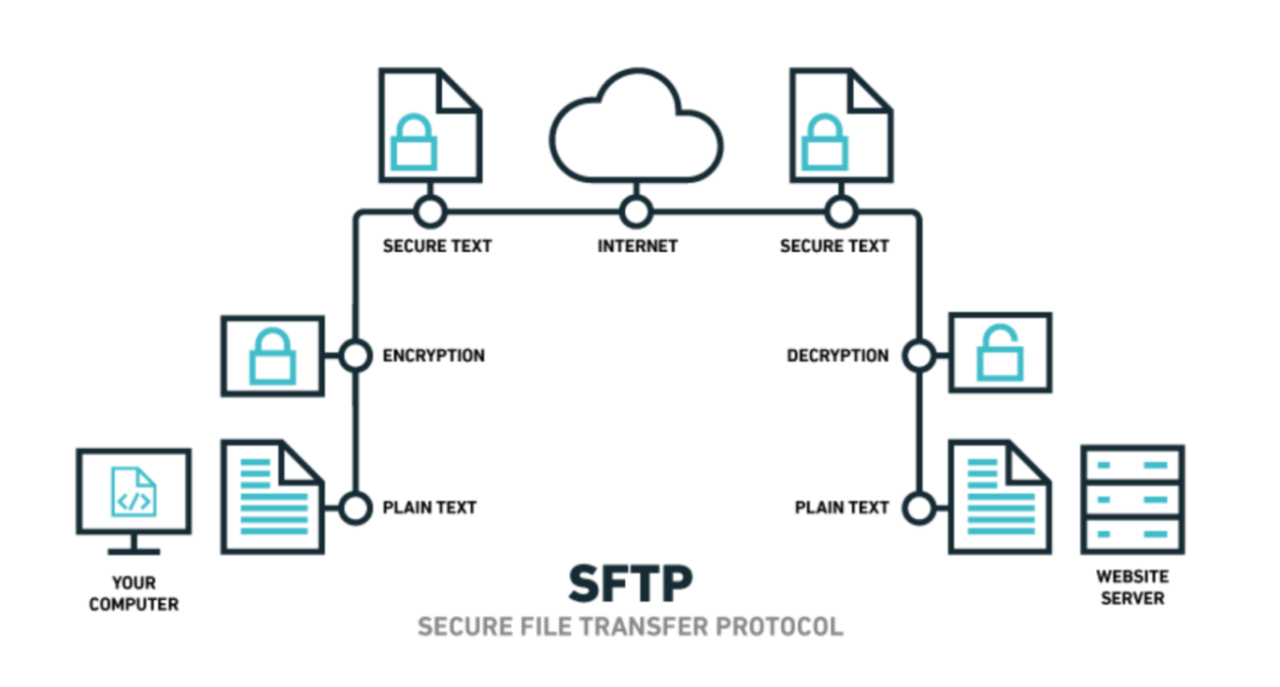
- Transfer your website files and databases to the cloud server.
- Use secure transfer methods (e.g., SFTP, rsync).
b. Update Configuration Files:
- Update configuration files (e.g., wp-config.php for WordPress) with new database credentials and server settings.
4. Test Thoroughly
a. Pre-Launch Testing:
- Verify that all content, images, and links are working correctly.
- Test forms, scripts, and dynamic elements.
b. Performance Testing:
- Use tools like GTmetrix, Pingdom, or Google PageSpeed Insights to test the speed and performance.
- Ensure that your website loads quickly and efficiently on the new server.
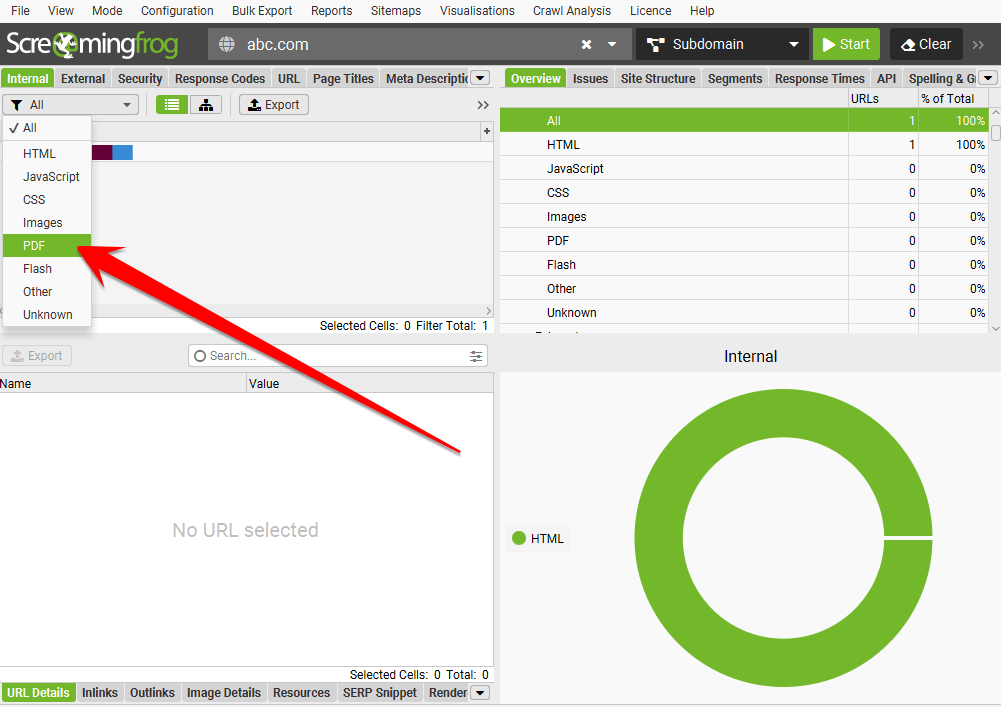
c. SEO Testing:
- Check for broken links and fix any issues using tools like Screaming Frog.
- Verify that your robots.txt and sitemap.xml files are correctly configured.
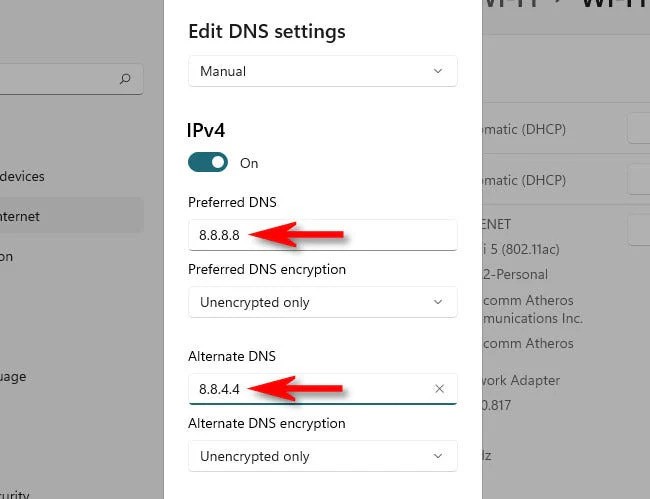
5. Update DNS Settings
a. Reduce TTL:
- Before updating DNS settings, reduce the Time to Live (TTL) value of your DNS records to minimize propagation time.
b. Change DNS Records:
- Update your DNS records to point to the new cloud server’s IP address.
- Verify that the changes have propagated correctly.
6. Monitor and Maintain SEO
a. Monitor Traffic and Rankings:
- Keep a close eye on your traffic and rankings using Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
- Look for any sudden drops in traffic or rankings.
b. Address Any Issues:
- If you notice any SEO issues, address them promptly. This could include fixing broken links, adjusting server settings, or resolving performance issues.
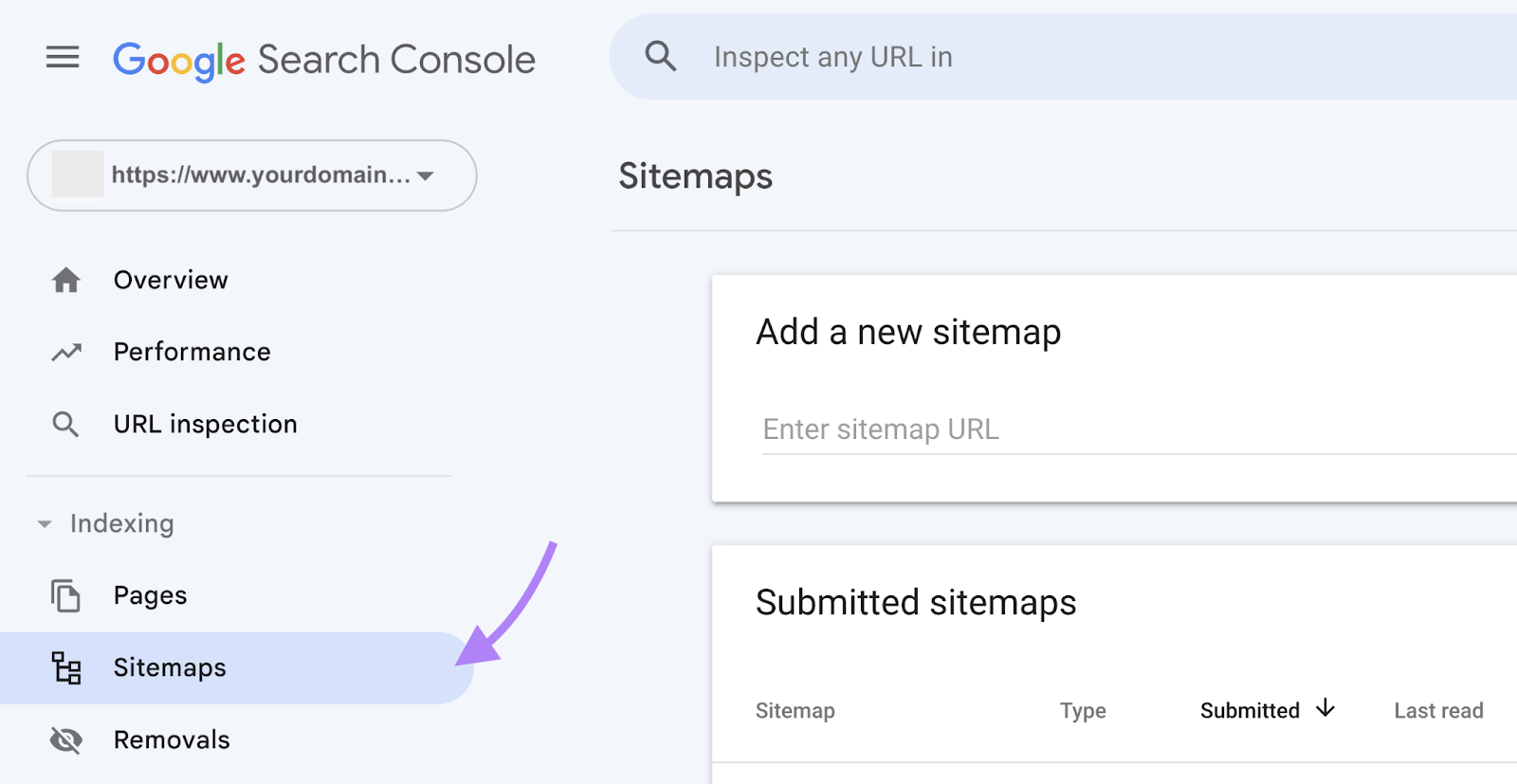
c. Submit a New Sitemap:
- Submit a new sitemap to Google Search Console to help search engines index your site on the new server.
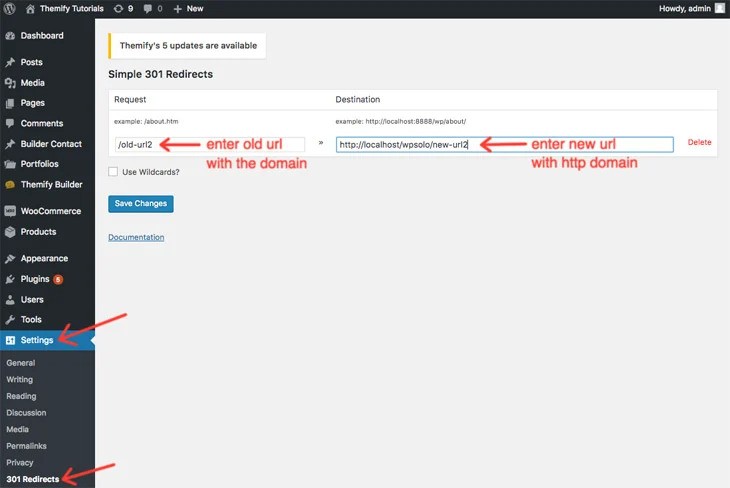
7. Implement 301 Redirects (If Necessary)
a. Redirect Old URLs:
- If your URLs change during the migration, implement 301 redirects from old URLs to new URLs.
- Ensure that all redirects are properly set up and tested.
b. Update Internal Links:
- Update internal links to point directly to the new URLs without relying on redirects.
8. Communicate with Stakeholders
a. Notify Users:
- Inform your users about the migration in advance. This helps manage expectations if there’s any downtime.
b. Collaborate with Your SEO Team:
- Ensure your SEO team is involved throughout the process to monitor and address any SEO concerns.
9. Post-Migration Optimization
a. Speed Optimization:
- Continuously optimize your site’s speed by compressing images, minifying code, and leveraging browser caching.
b. Security:
- Implement security measures like SSL certificates, firewalls, and regular security scans to protect your site.
10. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
a. Regular Audits:
- Conduct regular SEO audits to identify and fix issues.
- Monitor server performance and make adjustments as needed.
b. Keep Software Updated:
- Regularly update your CMS, plugins, and server software to ensure security and performance.
By following these steps, you can migrate to cloud hosting without compromising your SEO. Thorough planning, meticulous execution, and ongoing monitoring are key to maintaining your site’s SEO health during and after the migration.
Pros of Cloud Hosting Migration
1. Scalability:
- Benefit: Cloud hosting allows you to easily scale resources up or down based on your website’s traffic and needs.
- Example: During peak traffic times, such as Black Friday sales, you can increase server capacity to handle the surge in visitors.
2. Performance and Speed:
- Benefit: With advanced caching and global data centers, cloud hosting can significantly improve website loading times.
- Example: Faster loading speeds enhance user experience and can positively affect your SEO rankings.
3. Reliability and Uptime:
- Benefit: Cloud hosting providers typically offer high uptime guarantees, minimizing the risk of downtime.
- Example: Continuous availability ensures that your website remains accessible to users and search engine crawlers alike.
4. Cost Efficiency:
- Benefit: Pay-as-you-go pricing models ensure you only pay for the resources you use, potentially lowering overall hosting costs.
- Example: Smaller websites can save money by only using minimal resources during off-peak times.
Cons of Cloud Hosting Migration
1. Complexity:
- Drawback: The migration process can be complex and requires technical expertise.
- Example: Improper configuration or data transfer can lead to website downtime and loss of data.
2. Potential Downtime:
- Drawback: There is a risk of temporary downtime during the migration process.
- Example: Even a short period of unavailability can impact user experience and SEO rankings.
3. Initial Costs:
- Drawback: While long-term costs can be lower, the initial setup and migration can be expensive.
- Example: You may need to invest in professional services to ensure a smooth transition.
4. Learning Curve:
- Drawback: Adapting to a new hosting environment and managing cloud services can require a learning curve.
- Example: Your team may need training to effectively manage and optimize the new cloud infrastructure.
Impact of Losing SEO During Migration
If you lose SEO during the migration to cloud hosting, the consequences can be significant. A drop in search engine rankings can lead to decreased organic traffic, which directly affects your website’s visibility and potential revenue. Here’s what might happen:
1. Decreased Traffic:
- Your site may experience a sharp decline in organic traffic, reducing the number of visitors and potential customers.
2. Lower Revenue:
- With fewer visitors, your conversion rates and sales can suffer, impacting your overall revenue.
3. Reduced Brand Visibility:
- Lower rankings mean less exposure, making it harder for new users to discover your brand.
4. Rebuilding Efforts:
- Recovering lost rankings can take time and effort, requiring additional SEO campaigns and strategies to regain your position.
In essence, losing SEO during a migration can set back your digital marketing efforts, highlighting the importance of meticulous planning and execution to preserve your search engine standing.Top of Form

