In today’s digital age, accessibility is not just a buzzword; it’s a necessity. Ensuring that your WordPress website is accessible means that everyone, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with your site.
Accessibility isn’t just about compliance with legal standards; it’s about inclusivity and reaching the widest possible audience.
In this comprehensive guide on how to make your WordPress Website accessible, we’ll walk you through the significance of making your WordPress website accessible, catering to both beginners and experts, and provide a step-by-step process to achieve it.
The Significance of Accessibility: Why it Matters
Accessibility is crucial for several reasons:
1. Inclusivity:
Making your website accessible means ensuring that everyone, including people with disabilities, can access your content. It’s about creating a level playing field and embracing diversity.
2. Legal Compliance:
Many countries have laws and regulations that require websites to be accessible. Failure to comply can result in legal repercussions and discrimination lawsuits.
3. SEO Benefits:
Accessible websites tend to have better search engine rankings because they provide a better user experience for all users, including those using assistive technologies.
4. Expanded Audience Reach:
By making your website accessible, you open it up to a broader audience, potentially increasing traffic, engagement, and conversions.
Now, let’s delve into the step-by-step process of making your WordPress website accessible, catering to both beginners and experts.
Step 1: Choose an Accessible Theme
● Beginner Level:
When selecting a theme for your WordPress website, opt for one that prioritizes accessibility. Look for themes that follow accessibility best practices, such as high contrast colors, proper heading structures, and keyboard navigation compatibility.
● Expert Level:
If you’re experienced with web development, you can also customize your theme to enhance accessibility further.
This may involve modifying CSS stylesheets, ensuring proper HTML semantics, and integrating ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) roles and attributes.
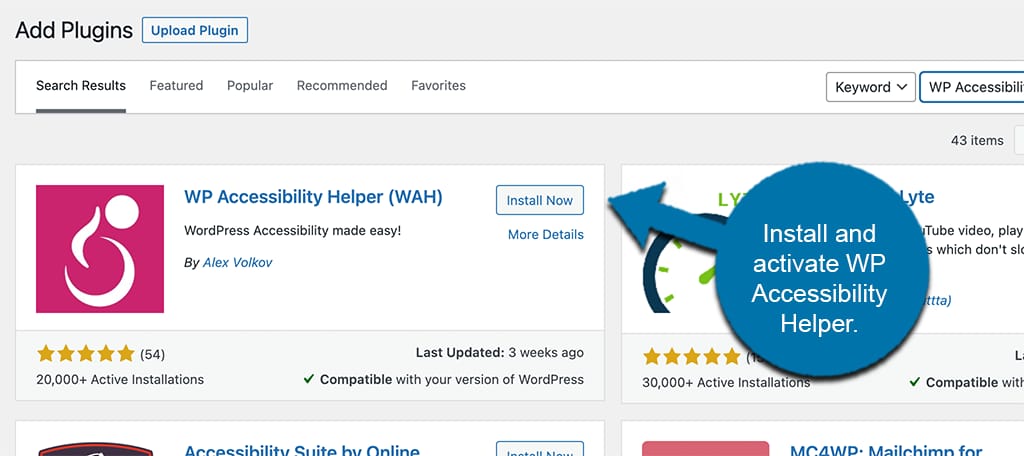
Step 2: Use Accessible Plugins
● Beginner Level:
Install plugins that enhance the accessibility of your website. Plugins like WP Accessibility add accessibility features such as skip links, keyboard navigation enhancements, and improved image alt text management without requiring any coding knowledge.
● Expert Level:
Develop custom plugins or extend existing ones to address specific accessibility requirements unique to your website. This might include creating custom keyboard shortcuts, optimizing forms for screen readers, or implementing ARIA landmarks for improved navigation.
Step 3: Optimize Images and Media
● Beginner Level:
Ensure all images on your website have descriptive alt text. Alt text provides a textual alternative to images, making them accessible to visually impaired users who rely on screen readers.
● Expert Level:
Compress images to reduce file size without compromising quality, ensuring faster load times for all users. Additionally, consider providing captions or transcripts for videos and audio content to accommodate users with hearing impairments.
Step 4: Create Semantic HTML
● Beginner Level:
Structure your content using proper HTML elements such as headings, paragraphs, lists, and semantic markup. This helps screen readers interpret the content correctly and improves overall accessibility.
● Expert Level:
Audit your website’s HTML code to identify and correct any semantic errors or structural issues. Use tools like WAVE (Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool) or Lighthouse in Google Chrome to identify accessibility issues and ensure compliance with best practices.
Step 5: Implement Keyboard Navigation
● Beginner Level:
Test your website’s navigation using only the keyboard. Ensure that users can navigate through all interactive elements, such as links, buttons, and form fields, using the Tab key.
● Expert Level:
Fine-tune keyboard navigation by adding focus styles to interactive elements and ensuring logical tab order throughout the website. Consider implementing custom keyboard shortcuts for frequently accessed features or functionality.
Step 6: Test with Accessibility Tools
● Beginner Level:
Use online accessibility testing tools like WAVE or AXE to identify common accessibility issues on your website. These tools provide detailed reports and recommendations for improving accessibility.
● Expert Level:
Conduct manual accessibility audits using screen readers and other assistive technologies to simulate the experience of users with disabilities. Address any usability barriers or issues uncovered during testing to ensure a seamless experience for all users.
Step 7: Provide Alternative Content
● Beginner Level:
Offer alternative content or formats for users who may have difficulty accessing certain types of content. For example, provide downloadable PDF versions of articles or transcripts for podcasts.
● Expert Level:
Develop dynamic content delivery mechanisms that adapt to users’ preferences and accessibility needs.
This might include offering customizable font sizes and color schemes or implementing text-to-speech functionality for reading long-form content aloud.
Step 8: Stay Updated and Educated
● Beginner Level:
Stay informed about accessibility best practices and guidelines by following reputable blogs, attending webinars, and participating in online forums and communities dedicated to web accessibility.
● Expert Level:
Contribute to the accessibility community by sharing your knowledge and expertise, participating in accessibility-related initiatives, and advocating for inclusive design practices within your organization and industry.
Conclusion:
By following these steps of how to make your WordPress Website accessible, both beginners and experts can make significant strides in improving the accessibility of their WordPress websites. Remember, accessibility is an ongoing process, so continue to monitor and update your website to ensure that it remains inclusive and user-friendly for all visitors.

